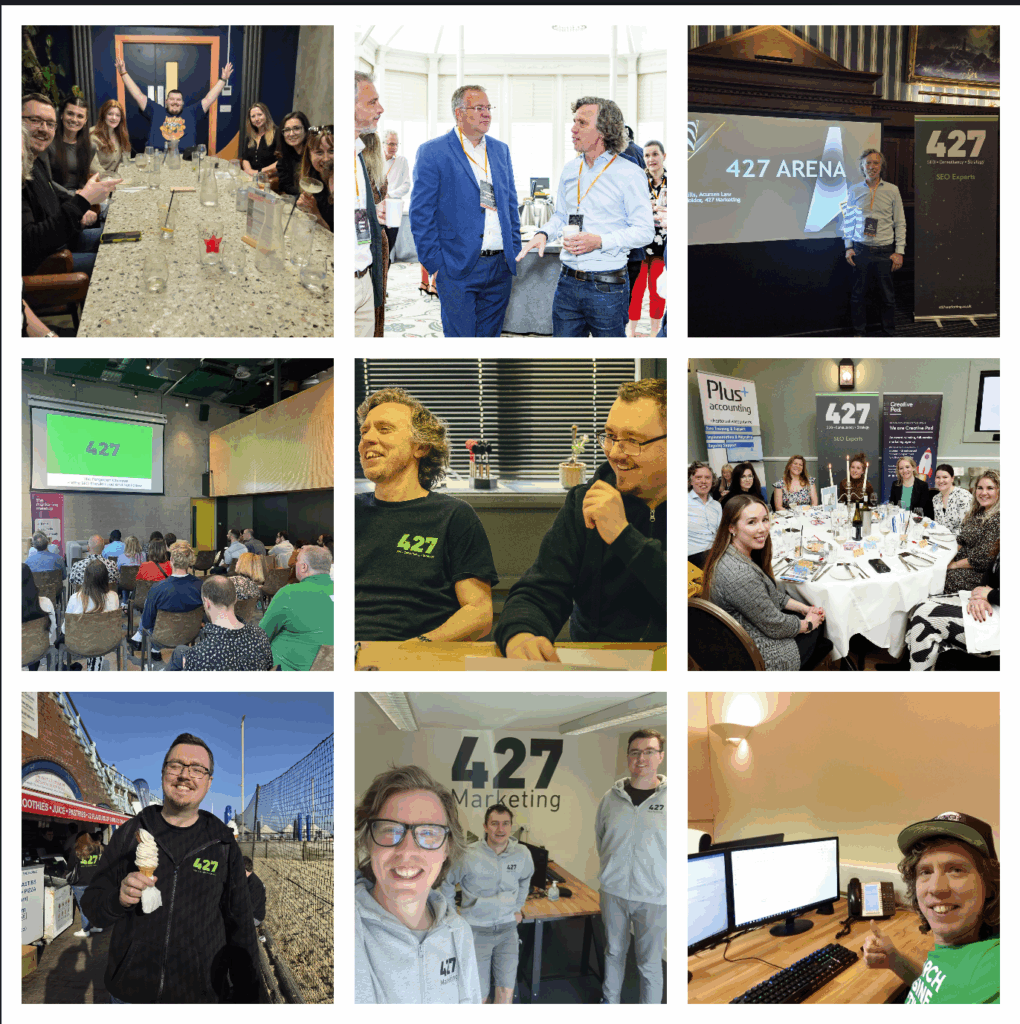

84 results


How to Connect Google Search Console to GA4

TOP 19 Local Business Directories

A guide to Google’s E-E-A-T

Removing Yourself From Google: Why, How and with What Success?

Deleting your personal info from Google just got easier
Image Optimisation
5 Ways to Optimise Your Content for Google Discover

What are rich snippets and how to get them

Everything You Need to Know About Link Rot

Should you target low volume and zero search volume keywords

How to check website accessibility
Award Winning SEO Agency
Startup & SME SEO Specialists
Highly Experienced Team
International & Enterprise SEO Provider
Award Winning SEO Agency
Startup & SME SEO Specialists
Highly Experienced Team
International & Enterprise SEO Provider
Award Winning SEO Agency
Startup & SME SEO Specialists
Highly Experienced Team
International & Enterprise SEO Provider
Award Winning SEO Agency
Startup & SME SEO Specialists
Highly Experienced Team
International & Enterprise SEO Provider
Award Winning SEO Agency
Startup & SME SEO Specialists
Highly Experienced Team
International & Enterprise SEO Provider
Award Winning SEO Agency
Startup & SME SEO Specialists
Highly Experienced Team
International & Enterprise SEO Provider
Award Winning SEO Agency
Startup & SME SEO Specialists
Highly Experienced Team
International & Enterprise SEO Provider
Award Winning SEO Agency
Startup & SME SEO Specialists
Highly Experienced Team
International & Enterprise SEO Provider
Award Winning SEO Agency
Startup & SME SEO Specialists
Highly Experienced Team
International & Enterprise SEO Provider
Award Winning SEO Agency
Startup & SME SEO Specialists
Highly Experienced Team
International & Enterprise SEO Provider
Award Winning SEO Agency
Startup & SME SEO Specialists
Highly Experienced Team
International & Enterprise SEO Provider
Award Winning SEO Agency
Startup & SME SEO Specialists
Highly Experienced Team
International & Enterprise SEO Provider
Award Winning SEO Agency
Startup & SME SEO Specialists
Highly Experienced Team
International & Enterprise SEO Provider
Award Winning SEO Agency
Startup & SME SEO Specialists
Highly Experienced Team
International & Enterprise SEO Provider
Award Winning SEO Agency
Startup & SME SEO Specialists
Highly Experienced Team
International & Enterprise SEO Provider
Award Winning SEO Agency
Startup & SME SEO Specialists
Highly Experienced Team
International & Enterprise SEO Provider
Award Winning SEO Agency
Startup & SME SEO Specialists
Highly Experienced Team
International & Enterprise SEO Provider
Award Winning SEO Agency
Startup & SME SEO Specialists
Highly Experienced Team
International & Enterprise SEO Provider
Award Winning SEO Agency
Startup & SME SEO Specialists
Highly Experienced Team
International & Enterprise SEO Provider
Award Winning SEO Agency
Startup & SME SEO Specialists
Highly Experienced Team
International & Enterprise SEO Provider
Award Winning SEO Agency
Startup & SME SEO Specialists
Highly Experienced Team
International & Enterprise SEO Provider
Award Winning SEO Agency
Startup & SME SEO Specialists
Highly Experienced Team
International & Enterprise SEO Provider
Award Winning SEO Agency
Startup & SME SEO Specialists
Highly Experienced Team
International & Enterprise SEO Provider
Award Winning SEO Agency
Startup & SME SEO Specialists
Highly Experienced Team
International & Enterprise SEO Provider
Award Winning SEO Agency
Startup & SME SEO Specialists
Highly Experienced Team
International & Enterprise SEO Provider
Award Winning SEO Agency
Startup & SME SEO Specialists
Highly Experienced Team
International & Enterprise SEO Provider
Award Winning SEO Agency
Startup & SME SEO Specialists
Highly Experienced Team
International & Enterprise SEO Provider
Award Winning SEO Agency
Startup & SME SEO Specialists
Highly Experienced Team
International & Enterprise SEO Provider
Award Winning SEO Agency
Startup & SME SEO Specialists
Highly Experienced Team
International & Enterprise SEO Provider
Award Winning SEO Agency
Startup & SME SEO Specialists
Highly Experienced Team
International & Enterprise SEO Provider
Award Winning SEO Agency
Startup & SME SEO Specialists
Highly Experienced Team
International & Enterprise SEO Provider
Award Winning SEO Agency
Startup & SME SEO Specialists
Highly Experienced Team
International & Enterprise SEO Provider
Award Winning SEO Agency
Startup & SME SEO Specialists
Highly Experienced Team
International & Enterprise SEO Provider
Award Winning SEO Agency
Startup & SME SEO Specialists
Highly Experienced Team
International & Enterprise SEO Provider
Award Winning SEO Agency
Startup & SME SEO Specialists
Highly Experienced Team
International & Enterprise SEO Provider
Award Winning SEO Agency
Startup & SME SEO Specialists
Highly Experienced Team
International & Enterprise SEO Provider
Award Winning SEO Agency
Startup & SME SEO Specialists
Highly Experienced Team
International & Enterprise SEO Provider
Award Winning SEO Agency
Startup & SME SEO Specialists
Highly Experienced Team
International & Enterprise SEO Provider
Award Winning SEO Agency
Startup & SME SEO Specialists
Highly Experienced Team
International & Enterprise SEO Provider
Award Winning SEO Agency
Startup & SME SEO Specialists
Highly Experienced Team
International & Enterprise SEO Provider
Award Winning SEO Agency
Startup & SME SEO Specialists
Highly Experienced Team
International & Enterprise SEO Provider




Stay in the loop
Newsletter sign up
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Nam vitae ante eu purus cursus aliquam. Pellentesque blandit viverra metus, a malesuada libero commodo eu.